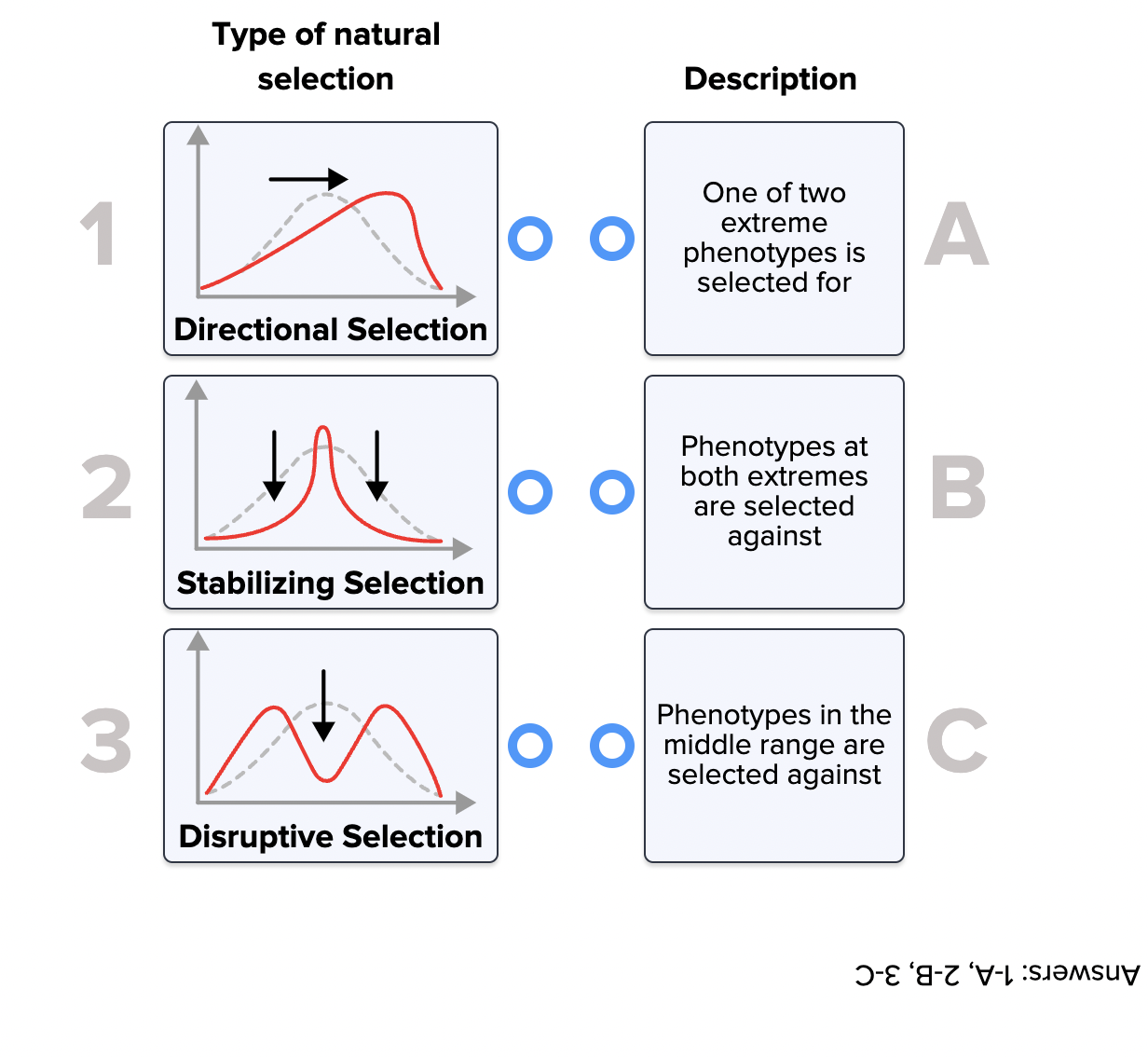
What Is Directional Selection Biology . the directional selection theory says that an extreme phenotype (characteristics or traits) is favored over other phenotypes and this causes the allele frequency (how often the variant of a gene shows up in a population) to shift over time in favor of the extreme phenotype. in directional selection, a population’s genetic variance shifts toward a new phenotype when exposed to environmental changes. directional selection is when individuals with traits on one side of the mean in their population survive better or. directional selection is a type of natural selection in which the phenotype (the observable. Learn how it works, see graphs,. directional selection is a type of natural selection in which a particular extreme phenotype is favored over other phenotypes, leading to a shift in the frequency. directional selection is a form of natural selection that favors extreme traits in response to environmental changes.
from www.ck12.org
directional selection is a form of natural selection that favors extreme traits in response to environmental changes. directional selection is when individuals with traits on one side of the mean in their population survive better or. the directional selection theory says that an extreme phenotype (characteristics or traits) is favored over other phenotypes and this causes the allele frequency (how often the variant of a gene shows up in a population) to shift over time in favor of the extreme phenotype. in directional selection, a population’s genetic variance shifts toward a new phenotype when exposed to environmental changes. Learn how it works, see graphs,. directional selection is a type of natural selection in which the phenotype (the observable. directional selection is a type of natural selection in which a particular extreme phenotype is favored over other phenotypes, leading to a shift in the frequency.
Natural Selection ( Read ) Biology CK12 Foundation
What Is Directional Selection Biology directional selection is a type of natural selection in which the phenotype (the observable. directional selection is a form of natural selection that favors extreme traits in response to environmental changes. Learn how it works, see graphs,. the directional selection theory says that an extreme phenotype (characteristics or traits) is favored over other phenotypes and this causes the allele frequency (how often the variant of a gene shows up in a population) to shift over time in favor of the extreme phenotype. directional selection is when individuals with traits on one side of the mean in their population survive better or. directional selection is a type of natural selection in which a particular extreme phenotype is favored over other phenotypes, leading to a shift in the frequency. directional selection is a type of natural selection in which the phenotype (the observable. in directional selection, a population’s genetic variance shifts toward a new phenotype when exposed to environmental changes.
From www.youtube.com
Directional Selection YouTube What Is Directional Selection Biology directional selection is when individuals with traits on one side of the mean in their population survive better or. directional selection is a type of natural selection in which the phenotype (the observable. directional selection is a form of natural selection that favors extreme traits in response to environmental changes. in directional selection, a population’s genetic. What Is Directional Selection Biology.
From www.biologyonline.com
Natural selection Biology Online Dictionary What Is Directional Selection Biology in directional selection, a population’s genetic variance shifts toward a new phenotype when exposed to environmental changes. directional selection is when individuals with traits on one side of the mean in their population survive better or. directional selection is a form of natural selection that favors extreme traits in response to environmental changes. Learn how it works,. What Is Directional Selection Biology.
From www.ck12.org
Natural Selection ( Read ) Biology CK12 Foundation What Is Directional Selection Biology Learn how it works, see graphs,. in directional selection, a population’s genetic variance shifts toward a new phenotype when exposed to environmental changes. directional selection is when individuals with traits on one side of the mean in their population survive better or. directional selection is a type of natural selection in which the phenotype (the observable. . What Is Directional Selection Biology.
From www.slideshare.net
Directional Selection What Is Directional Selection Biology in directional selection, a population’s genetic variance shifts toward a new phenotype when exposed to environmental changes. directional selection is a form of natural selection that favors extreme traits in response to environmental changes. the directional selection theory says that an extreme phenotype (characteristics or traits) is favored over other phenotypes and this causes the allele frequency. What Is Directional Selection Biology.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Natural Selection and Speciation PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4158534 What Is Directional Selection Biology directional selection is a form of natural selection that favors extreme traits in response to environmental changes. directional selection is when individuals with traits on one side of the mean in their population survive better or. the directional selection theory says that an extreme phenotype (characteristics or traits) is favored over other phenotypes and this causes the. What Is Directional Selection Biology.
From www.visiblebody.com
Mechanisms of Evolution What Is Directional Selection Biology the directional selection theory says that an extreme phenotype (characteristics or traits) is favored over other phenotypes and this causes the allele frequency (how often the variant of a gene shows up in a population) to shift over time in favor of the extreme phenotype. Learn how it works, see graphs,. in directional selection, a population’s genetic variance. What Is Directional Selection Biology.
From www.britannica.com
Disruptive selection biology Britannica What Is Directional Selection Biology directional selection is a type of natural selection in which the phenotype (the observable. directional selection is when individuals with traits on one side of the mean in their population survive better or. in directional selection, a population’s genetic variance shifts toward a new phenotype when exposed to environmental changes. Learn how it works, see graphs,. . What Is Directional Selection Biology.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Evolution Selection and Speciation PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID209710 What Is Directional Selection Biology Learn how it works, see graphs,. in directional selection, a population’s genetic variance shifts toward a new phenotype when exposed to environmental changes. directional selection is a type of natural selection in which the phenotype (the observable. directional selection is a form of natural selection that favors extreme traits in response to environmental changes. directional selection. What Is Directional Selection Biology.
From ar.inspiredpencil.com
Directional Selection What Is Directional Selection Biology Learn how it works, see graphs,. directional selection is a form of natural selection that favors extreme traits in response to environmental changes. directional selection is a type of natural selection in which a particular extreme phenotype is favored over other phenotypes, leading to a shift in the frequency. directional selection is when individuals with traits on. What Is Directional Selection Biology.
From biologydictionary.net
Directional Selection, Stabilizing Directional and Disruptive Selection What Is Directional Selection Biology the directional selection theory says that an extreme phenotype (characteristics or traits) is favored over other phenotypes and this causes the allele frequency (how often the variant of a gene shows up in a population) to shift over time in favor of the extreme phenotype. directional selection is a form of natural selection that favors extreme traits in. What Is Directional Selection Biology.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Mechanisms of evolution PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1995354 What Is Directional Selection Biology directional selection is a type of natural selection in which a particular extreme phenotype is favored over other phenotypes, leading to a shift in the frequency. directional selection is when individuals with traits on one side of the mean in their population survive better or. directional selection is a form of natural selection that favors extreme traits. What Is Directional Selection Biology.
From www.pinterest.com
Directional Selection Easy Science Easy science, The selection, Natural selection What Is Directional Selection Biology directional selection is a type of natural selection in which the phenotype (the observable. in directional selection, a population’s genetic variance shifts toward a new phenotype when exposed to environmental changes. directional selection is when individuals with traits on one side of the mean in their population survive better or. directional selection is a type of. What Is Directional Selection Biology.
From slideplayer.com
Types of Selection. ppt download What Is Directional Selection Biology directional selection is a type of natural selection in which the phenotype (the observable. directional selection is a type of natural selection in which a particular extreme phenotype is favored over other phenotypes, leading to a shift in the frequency. the directional selection theory says that an extreme phenotype (characteristics or traits) is favored over other phenotypes. What Is Directional Selection Biology.
From leology.weebly.com
Evolution Leology What Is Directional Selection Biology directional selection is a type of natural selection in which a particular extreme phenotype is favored over other phenotypes, leading to a shift in the frequency. directional selection is a form of natural selection that favors extreme traits in response to environmental changes. in directional selection, a population’s genetic variance shifts toward a new phenotype when exposed. What Is Directional Selection Biology.
From bio1510.biology.gatech.edu
Evolution by Natural Selection Biological Principles What Is Directional Selection Biology Learn how it works, see graphs,. in directional selection, a population’s genetic variance shifts toward a new phenotype when exposed to environmental changes. directional selection is a form of natural selection that favors extreme traits in response to environmental changes. directional selection is when individuals with traits on one side of the mean in their population survive. What Is Directional Selection Biology.
From mauricio-bogspotmitchell.blogspot.com
Which Is the Best Definition of Directional Selection What Is Directional Selection Biology directional selection is a type of natural selection in which a particular extreme phenotype is favored over other phenotypes, leading to a shift in the frequency. directional selection is a form of natural selection that favors extreme traits in response to environmental changes. directional selection is a type of natural selection in which the phenotype (the observable.. What Is Directional Selection Biology.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Types of Natural Selection PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2180834 What Is Directional Selection Biology in directional selection, a population’s genetic variance shifts toward a new phenotype when exposed to environmental changes. the directional selection theory says that an extreme phenotype (characteristics or traits) is favored over other phenotypes and this causes the allele frequency (how often the variant of a gene shows up in a population) to shift over time in favor. What Is Directional Selection Biology.
From mavink.com
4 Types Of Natural Selection What Is Directional Selection Biology directional selection is a type of natural selection in which a particular extreme phenotype is favored over other phenotypes, leading to a shift in the frequency. in directional selection, a population’s genetic variance shifts toward a new phenotype when exposed to environmental changes. directional selection is a form of natural selection that favors extreme traits in response. What Is Directional Selection Biology.